August 21, 2025
What Is Industrial Automation?
Industrial automation offers significant benefits for multiple industries. According to research firm McKinsey, 97% of companies say automation will improve output quality, and 95% say it will increase production and delivery speed.
The challenge? Effective application. With a host of physical, digital, and hybrid automation solutions now available, manufacturers need to design and implement automation strategies that deliver both short-term benefits and long-term gains, all while staying within budget.
In this piece, we’ll break down the basics of industrial automation and the key technologies that support it. Then, we’ll look at the major benefits and potential challenges in automation adoption and offer practical strategies to help ensure automated systems deliver ROI.
Introduction to Industrial Automation
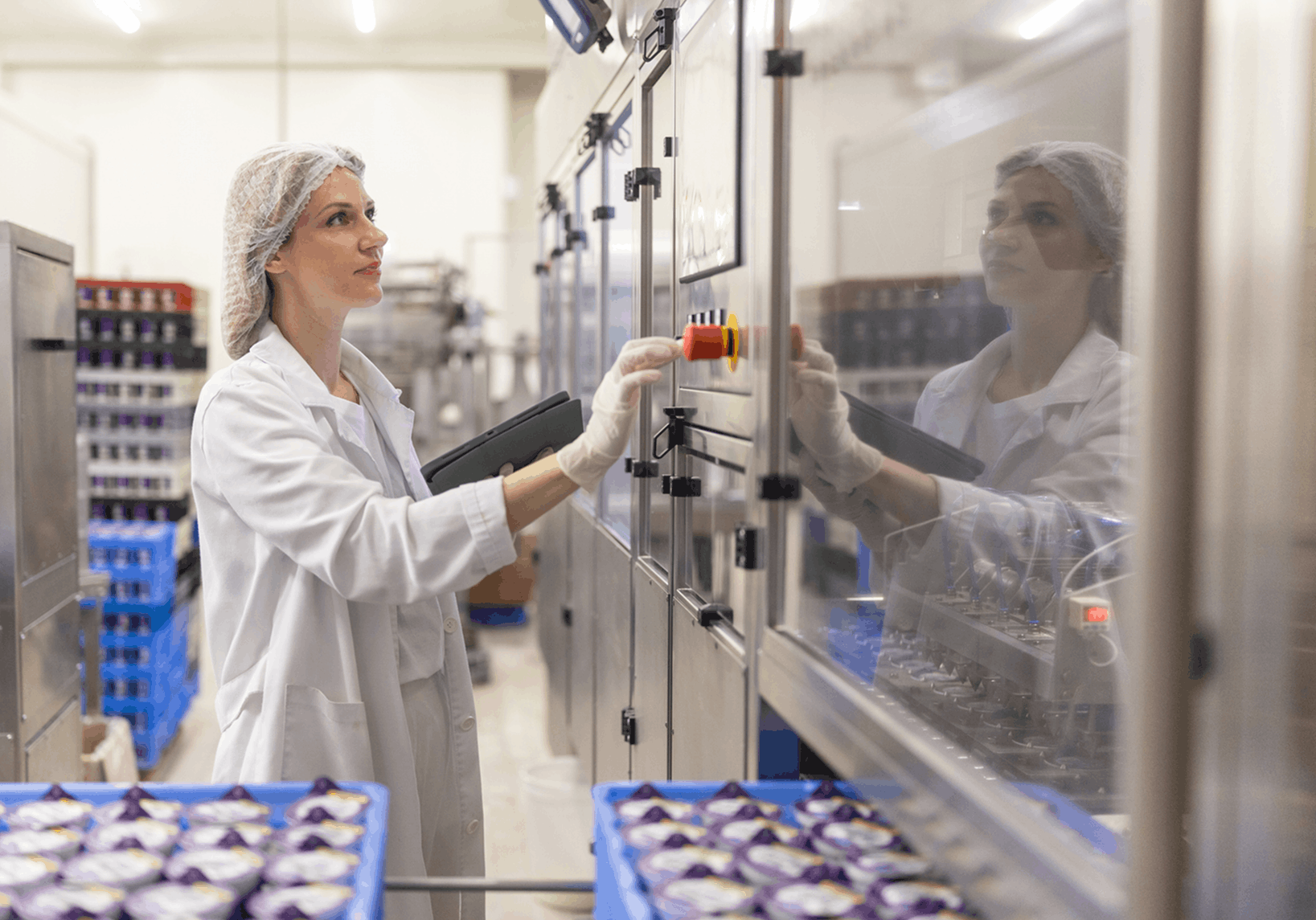
Industrial automation uses technology to improve production speed, quality, and safety by reducing or eliminating manual tasks.
For example, many automotive manufacturers now use robots to perform both simple and complex assembly tasks. Food and beverage companies, meanwhile, may integrate connected sensors to track machine metrics such as temperature, pressure, friction, and overall throughput.
Automation began with the first industrial revolution, which was characterized by the use of machines.
For example, the 19th century saw the rise of mechanical looms, which used punched cards to automate the weaving process and produce complex designs beyond human skill. This set the stage for Henry Ford’s assembly line, which helped establish the role of product consistency in automation.
The second industrial revolution introduced technologies such as electric control systems and programmable logic controllers (PLCs), which could be reprogrammed as needed to take on new tasks.
The digital, or third, industrial revolution followed and focused on integrating software solutions and connected networks into manufacturing environments. This provided improved visibility and control over production processes.
In 2015, the convergence of software solutions, physical devices, and emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) gave rise to the fourth industrial revolution, also known as Industry 4.0, or 4IR.
Key Technologies in Industrial Automation
Industrial automation depends on several key technologies.
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is the foundation of artificial intelligence. ML algorithms can be trained using large datasets to perform specific functions and make decisions based on available information.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The IIoT includes sensors, actuators, and other connected devices that perform key operations and deliver critical insights.
For example, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) can continually monitor inputs from temperature, pressure, and friction sensors and then take action based on this information, such as opening valves or reducing motor speeds.
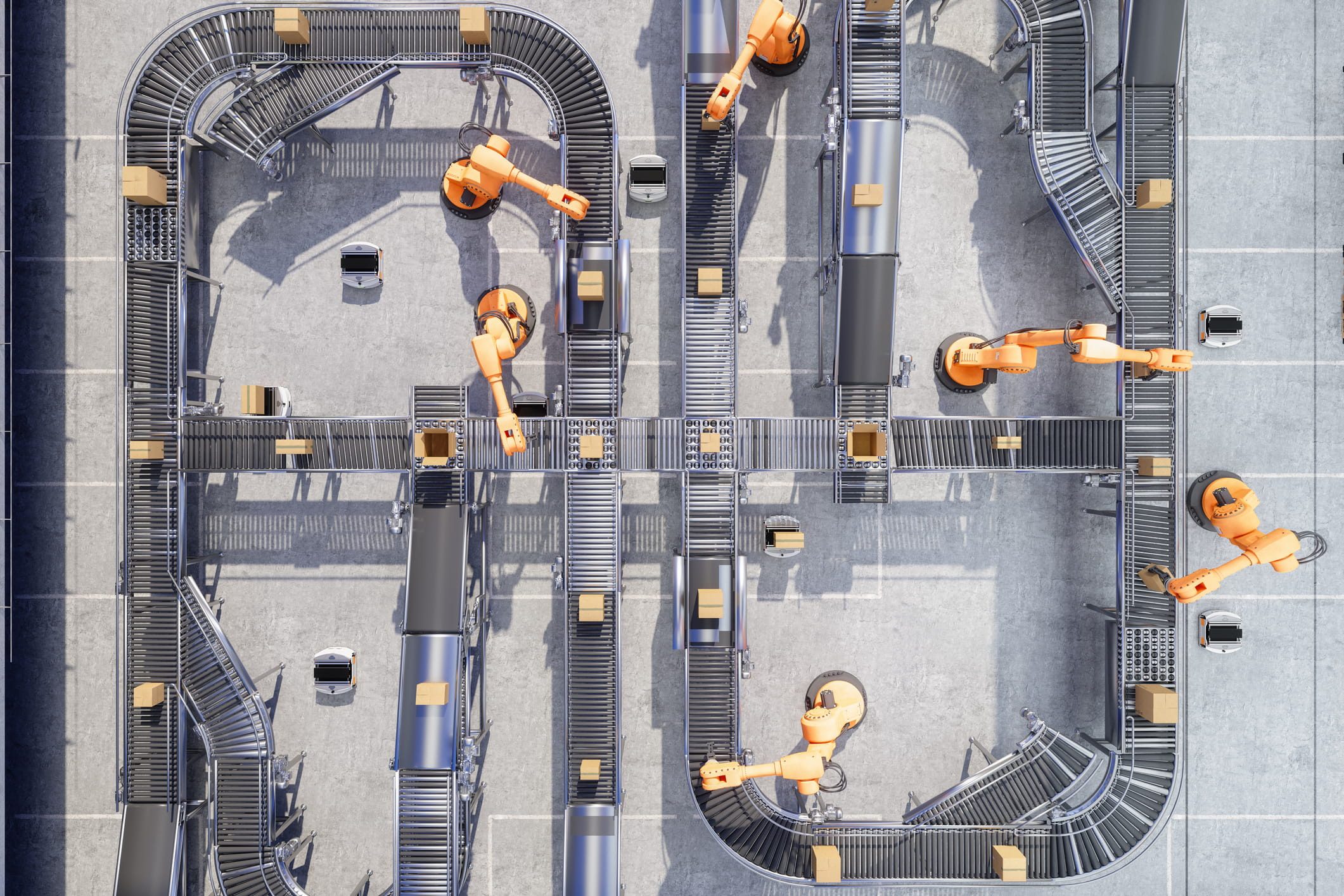
Robotics & Motion Control
Common uses of robotics in automation include fixed-point production-line robots capable of assembling complex components and mobile robots that retrieve and deliver materials from inventory.
Benefits of Automation in Manufacturing
One of the most obvious benefits of process automation in manufacturing is improved efficiency. By reducing or removing manual tasks, companies can shorten production times and enhance worker safety.
Automation also offers additional benefits.
- Cost reduction: By implementing automation, firms can limit the need for re-manufacturing due to failed quality checks and reduce time lost to machine failures or worker injuries. More uptime and fewer failures translate into cost savings
- Quality improvement: Connected production line robots and PLCs can be programmed to complete specialized tasks quickly and accurately. This consistency enables higher-quality outputs and reduces material waste.
- Digital transformation: Automation supports digital transformation by reducing reliance on manual data tracking and recording. Industrial automation solutions bridge physical and digital systems to deliver enhanced visibility.
Consider an Automaker
By using a combination of six-axis robotic arms for assembly, connected sensors for condition monitoring, and machine learning for data analysis, the automotive manufacturer can streamline production, identify areas for improvement, and measure the impact of changes.
Challenges and Considerations in Adopting Automation
As Industry 4.0 continues to gain traction, it’s important for companies to recognize and address the challenges associated with automation adoption.
One of the most common challenges is high initial costs. Robots, PLCs, and sensors often represent significant capital investments.
In addition, existing networks may not provide sufficient bandwidth or throughput to handle large-scale IIoT connections, requiring further investment in IT infrastructure.
To help manage these costs, organizations should assess current processes and operational needs to ensure automation investments target the most impactful areas.
Skill gaps and integration challenges are also common. New technologies often require skill sets that may not already exist within the organization.
While teams may adapt with time, productivity can suffer without proper training.
To mitigate this risk, training should be prioritized before deploying new devices or software solutions, giving staff hands-on exposure to automation tools.
Integration timelines can also present challenges. If integration doesn’t go as planned, manufacturers may need to pause or roll back deployments to identify root causes.
A phased implementation strategy can help reduce risk by breaking automation efforts into smaller, manageable stages.
Some employees may be concerned about job displacement. Companies can address these concerns by emphasizing collaboration rather than replacement.
For example, many companies deploy collaborative robots, or cobots, that work alongside human operators. Cobots typically handle repetitive or hazardous tasks, allowing staff to focus on higher-value work.
Advance Your Operations With Smarter Automation
Industrial automation systems have the potential to transform manufacturing operations. When paired with robust infrastructure and reliable connectivity, automation can enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and improve worker safety.
However, effective automation requires careful planning. Manufacturers must evaluate existing infrastructure, workforce capabilities, and areas where automation will deliver the most value.
EOSYS can help. Our industrial automation solutions span feasibility studies, system design, configuration and planning, startup, and ongoing support. That’s the EOSYS difference. We help clients from initial deployment through long-term monitoring and management.
Ready to explore the automation advantage?